Wansu Wang
Co-habitation
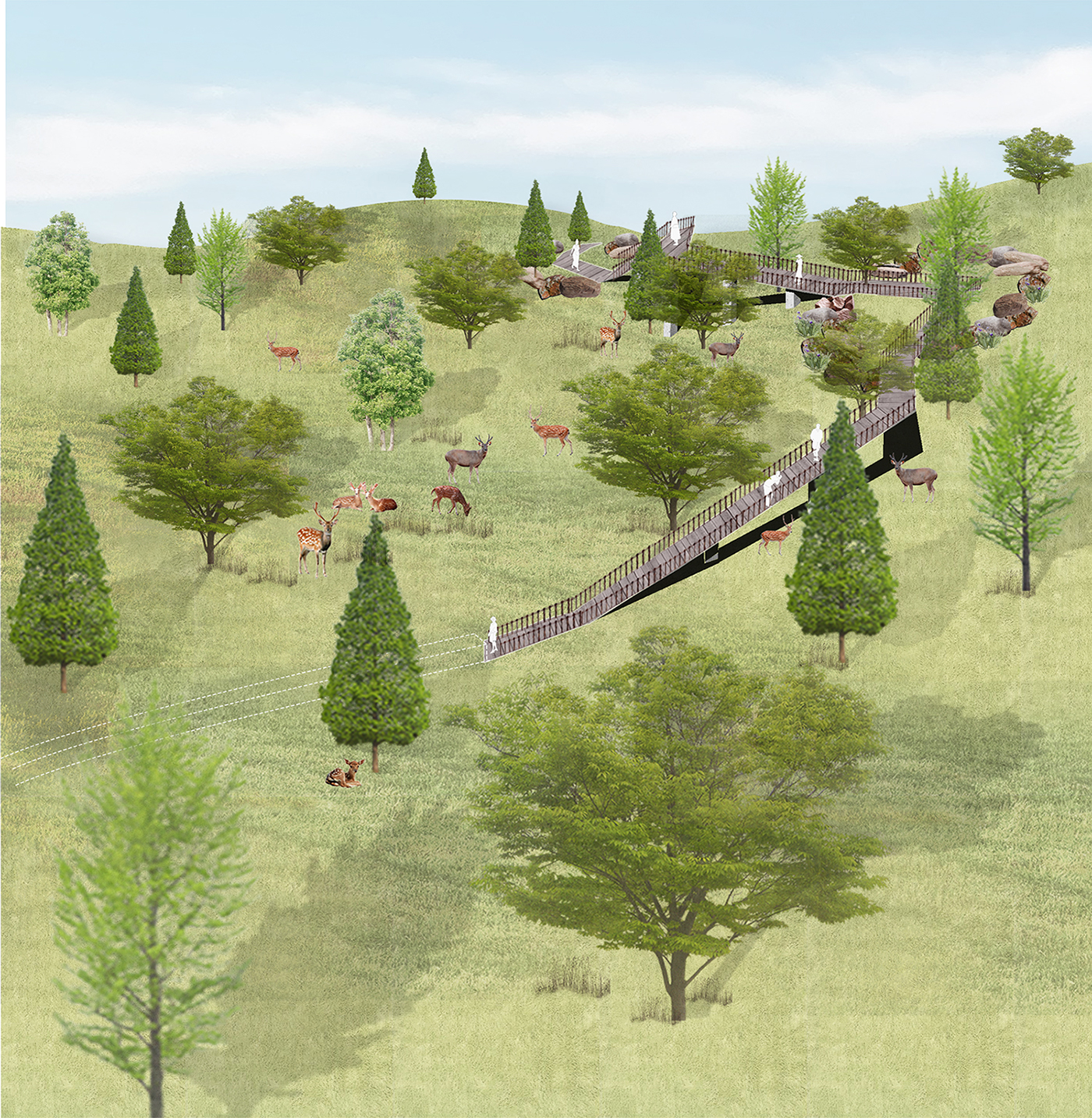
Establishing a safe and healthy living environment for human and nature in Dalian
According to a World Health Organization report, 75% of new infectious diseases are zoonotic, which means infected animals could pass virus to humans by direct or indirect contact. However, the natural habitat area in Dalian has been reduced through fragmentation due to urbanization, which leads to the exposure human settlements to specific species.
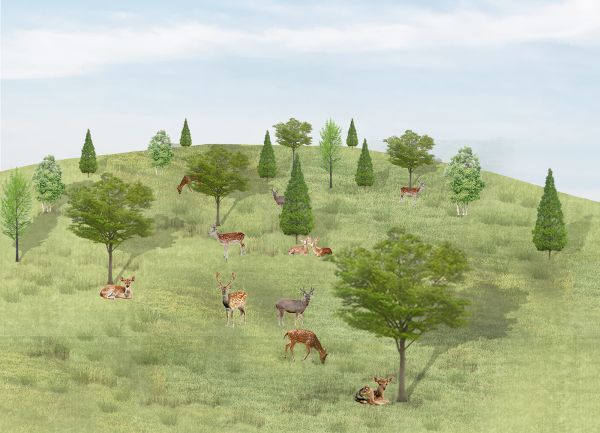
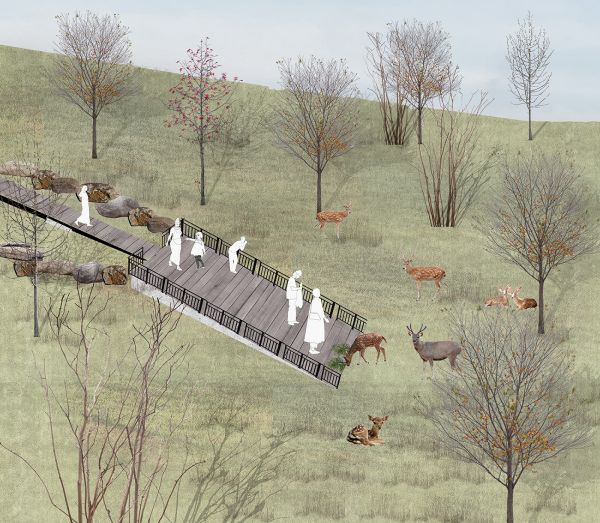
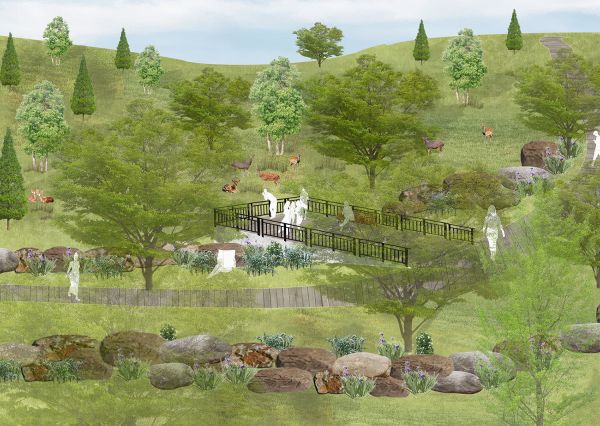
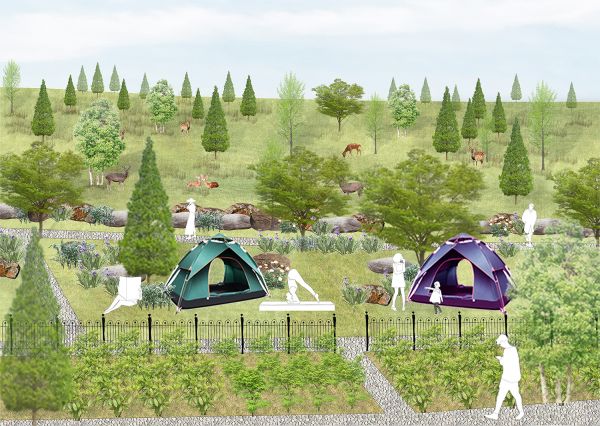
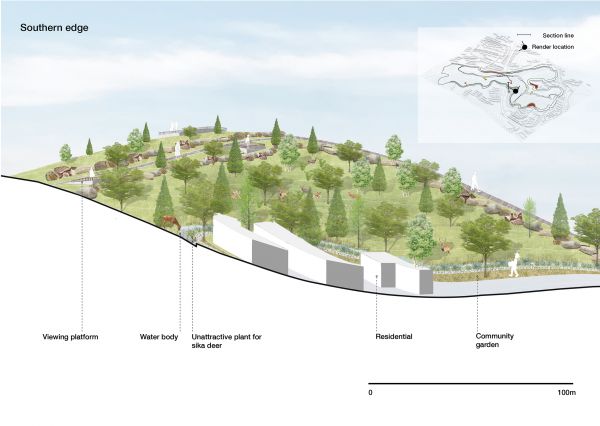
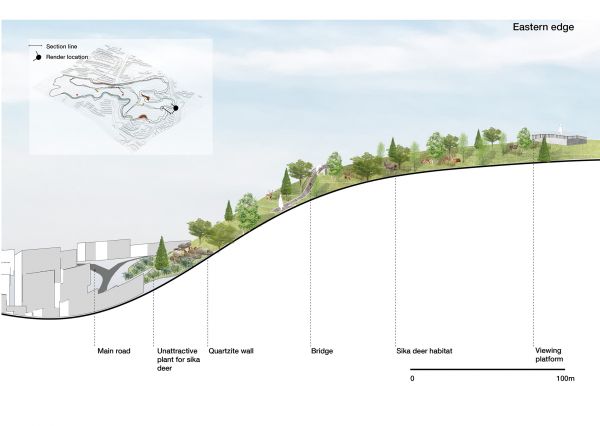
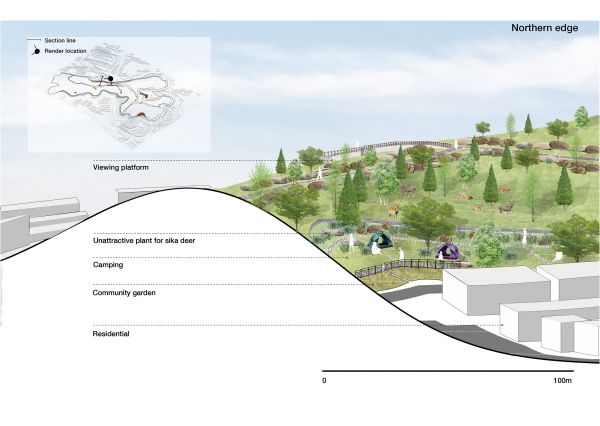
The thesis establishes co-habitation space for human and nature through the careful adaptation of spaces that promote appropriate and healthy interactivity. The local people and tourists can explore the natural environment without impacting fauna living and activities in habitat. The design adapts existing topography to create ‘terraces’ as buffer zone to mitigate boundaries between the deer’s habitat and residential suburbs.